Research
HOME > Research > Research Outputs
Research Outputs
Autonomous Driving Vehicles
VDC Lab autonomous driving demo (KAIST munji campus)
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping)
- Though satellite-aided localization such as global positioning system(GPS) provides localization bounded in global coordinate, it cannot provide lane-level accuracy of localization because of the interference of signals due to skyscrapers in an urban area.
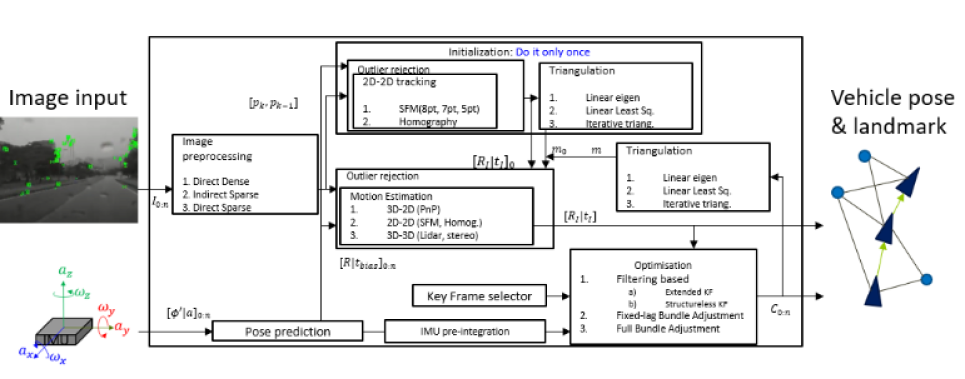
- By developing a camera and inertial fusion SLAM algorithm, it can provide accurate localization data and surrounding landmarks without GPS.
Deep learning-based 3D object detection
- 3D object detection is a task to detect 3d position and size of surrounding dynamic/static objects. Information of detected objects is used to plan the future maneuver of autonomous vehicles.
- Camera-Radar sensor fusion-based deep learning robust 3D object detection network using gating network

GRIF Net (IROS 2020)
Published Literature
- Kim et al., "Deep Learning based Vehicle Position and Orientation Estimation via Inverse Perspective Mapping Image”, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2020
- Kim et al., “GRIF Net : Gated Region of Interest Fusion Network for Robust 3D Object Detection from Radar Point Cloud and Monocular Image”, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020
- Kim et al., "Low-level Sensor Fusion for 3D Vehicle Detection using Radar Range-Azimuth Heatmap and Monocular Image", AFCV Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), 2020
Deep learning-based vehicle motion prediction
- Predicting the motion of vehicles is essential in order to plan the path for the autonomous vehicle
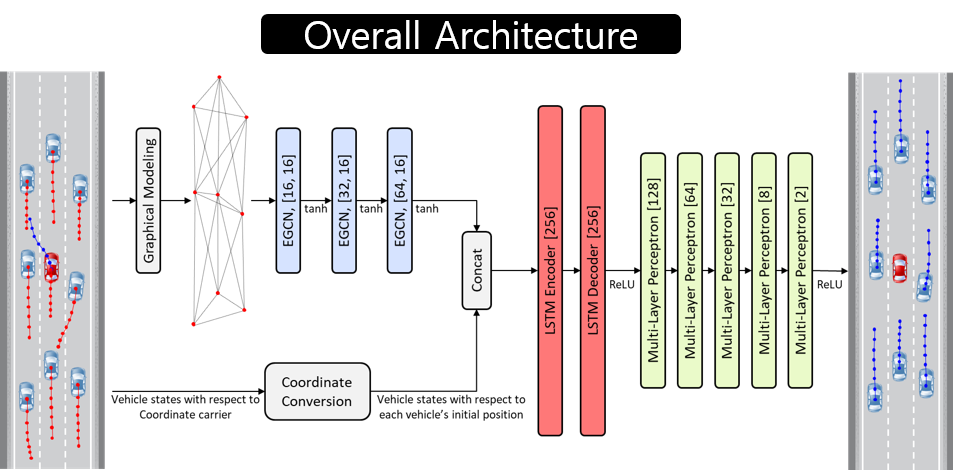
Architecture of SCALE-Net
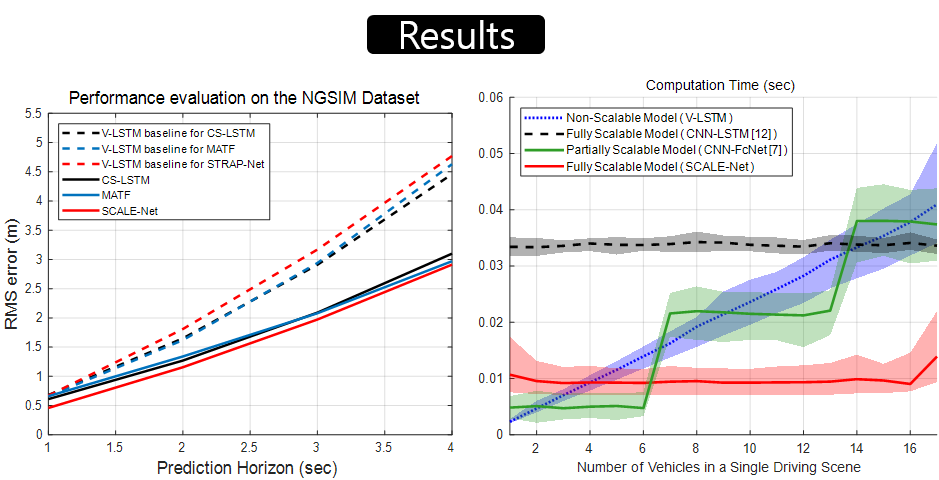
Motion prediction results based on SCALE-Net
SCALE-Net (IROS 2020)
- Various deep learning-based (EGCN, LSTM, etc.) method is applied for the accurate motion prediction model
- Not only for the accuracy but also for the scalability of the number of surrounding vehicles is considered in the motion prediction models
Published LIterature
- Jeon et al., “Traffic Scene Prediction via Deep Learning: Introduction of Multi-Channel Occupancy Grid Map as a Scene Representation”, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2018
- Yoon et al., “Predictive Cruise Control using Radial Basis Function Network-based Vehicle Motion Prediction and Chance Constrained Model Predictive Control”, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019
- Kim et al., “RECUP Net: RECUrsive Prediction Network for Surrounding Vehicle Trajectory Prediction with Future Trajectory Feedback”, IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2020
- Jeon et al., “SCALE-Net: Scalable Vehicle Trajectory Prediction Network under Random Number of Interacting Vehicles via Edge-enhanced Graph Convolutional Neural Network” IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020
Reinforcement learning-based vehicle path planning
- Research for the vehicle path planning via reinforcement learning
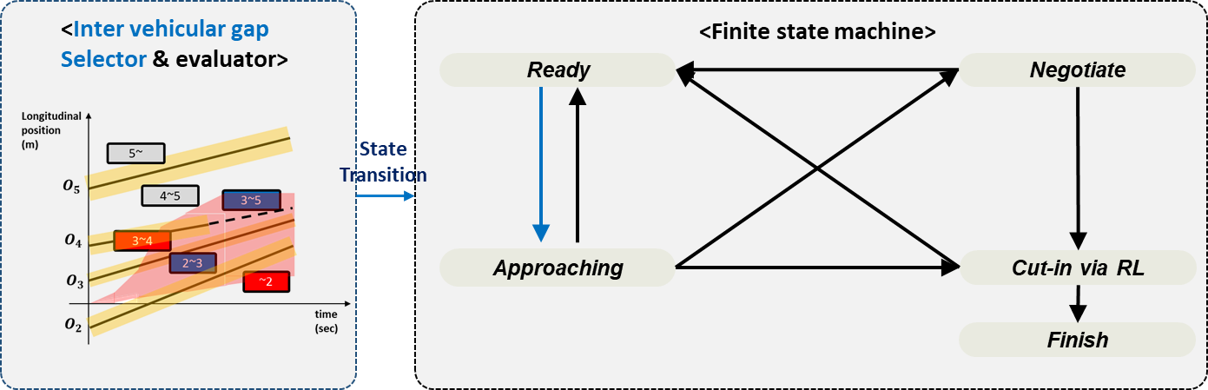
Decision making via finite state machine
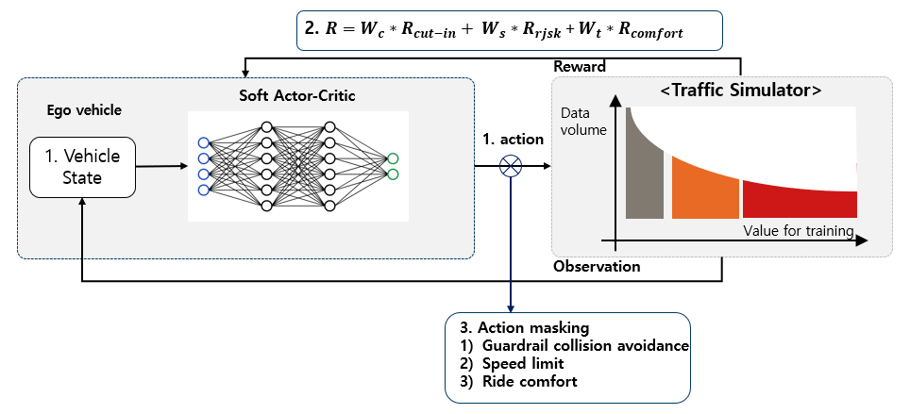
Path planning based on policy-based RL
- Path planning algorithm development for the lane-merging of an autonomous vehicle via a finite state machine and policy-based RL
- improvement in the lane merge success rate and collision avoidance rate (99.92% of collision avoidance rate and 77.18 % of cut-in success rate in the level 6 traffic situation)
Electric Powertrain
HEV architecture studies
- Power-split hybrids are suitable for both hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles thanks to their potential to achieve a high performing EV mode as well as a very efficient hybrid mode

The comprehensive design process of power-split hybrid electric vehicles
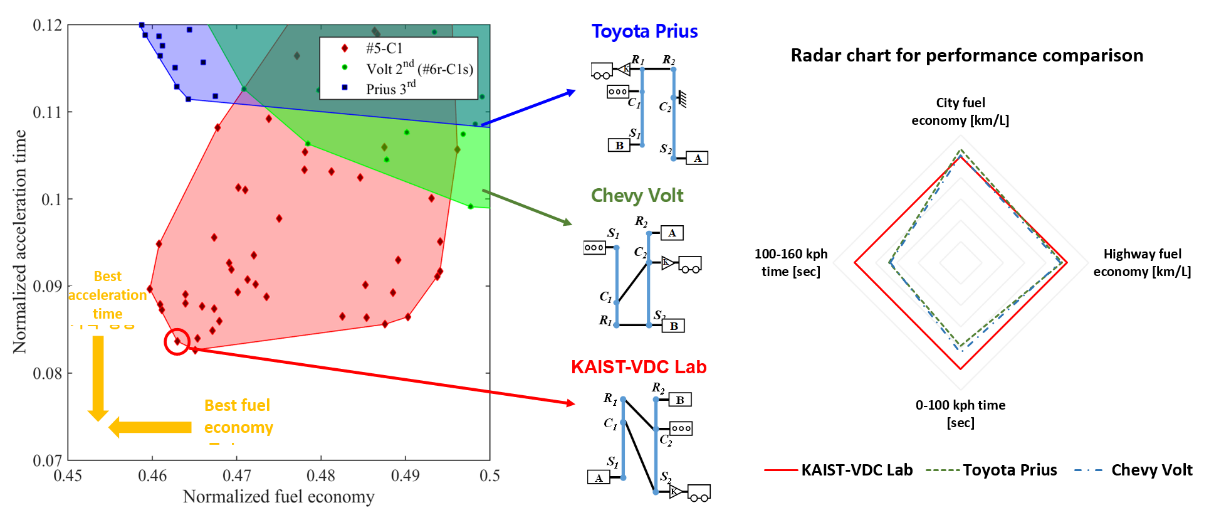
Performance Assessment Map (designs toward left bottom side have outstanding performance)
- An innovative search method was developed to find globally optimal (i.e. super-efficient and fun-to-drive) power-split hybrid powertrain architectures by using the virtual design space, which dramatically reduces the performance evaluation time from 114,000 years (if done within the physical design space) down to just seven days.
- A few novel power-split hybrid configurations with world-class fuel economy and acceleration performance were revealed (i.e. 27.8% faster than Toyota Prius and 26.2% faster and 3.3% more efficient than Chevy Volt.).
Published Literature
- Kang et al., “Systematic Design of Input-and Output-Split Hybrid Electric Vehicles With a Speed Reduction/Multiplication Gear Using Simplified-Lever Model”, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019
- Kim et al., “Comprehensive Design Methodology of Compound-Split Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Introduction of the Compound Lever as a Design Tool” IEEE Access, 2019
- Barhoumi et al,. “Automatic generation of design space conversion maps and its application for the design of compound split hybrid powertrains” Journal of Mechanical Design, 2018
- Barhoumi & Kum, “Automatic enumeration of feasible kinematic diagrams for split hybrid configurations with a single planetary gear” Journal of Mechanical Design, 2017
- Kim & Kum. “Comprehensive design methodology of input-and output-split hybrid electric vehicles: In search of optimal configuration” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016
- Barhoumi et al., “Compound lever based optimal configuration selection of compound-split hybrid vehicles” SAE Technical Paper, 2017
- Kim et al., “Impact of speed reduction (multiplication) gear on the performance of input-and output-split hybrid electric vehicles” SAE Technical Paper, 2017
Dog clutch research
- The dog clutch is introduced in VDC Lab’s Electric Powertrain team as a good alternative to the friction clutch.
- Dog clutch is a compact, lighter, and cheaper device as it does not use the hydraulic system, and has a higher power transfer efficiency as it engages by interference rather than frictions, which implies the absence of slip.
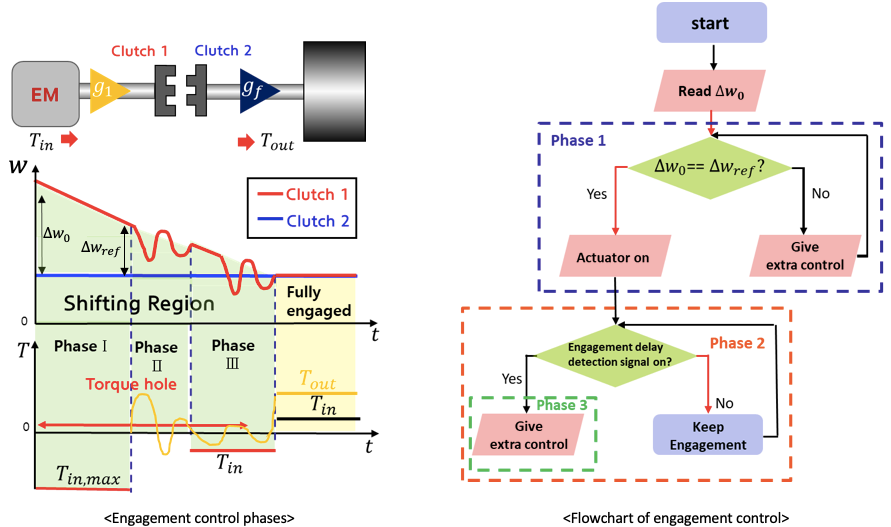
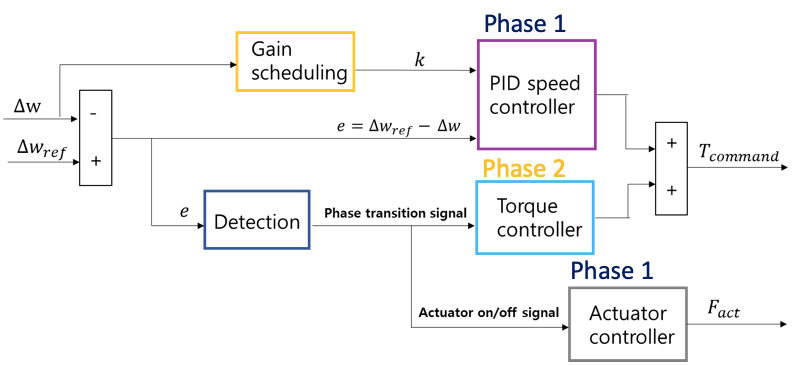
Dog clutch engagement controller
- A physics-based dog clutch model considering various design parameters such as taper angle, backlash angle, and teeth width is developed.
- A dog clutch control algorithm, which allows the approach of the relative speed to profitable speed ranges and the prevention of engagement delays (e.g. baulking and bounce back) was developed. The proposed controller improves the peak value of engagement completion time up to 60%.
Engine start control for parallel HEVs
- There exist various architectures of pre-transmission parallel hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) depending on the type and size of the starter motor(s).
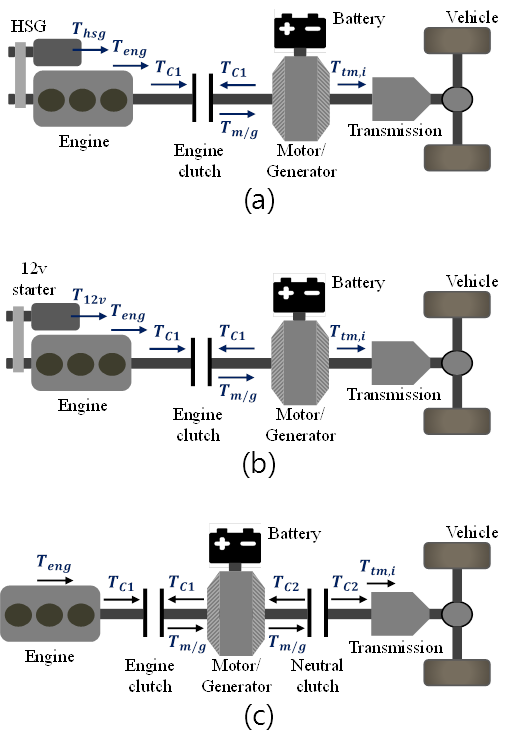
Structure diagram of the pre-transmission parallel HEV with various starter motors. (a) P0-P2 type. (b) 12v+P2 type. (c) P2 only type
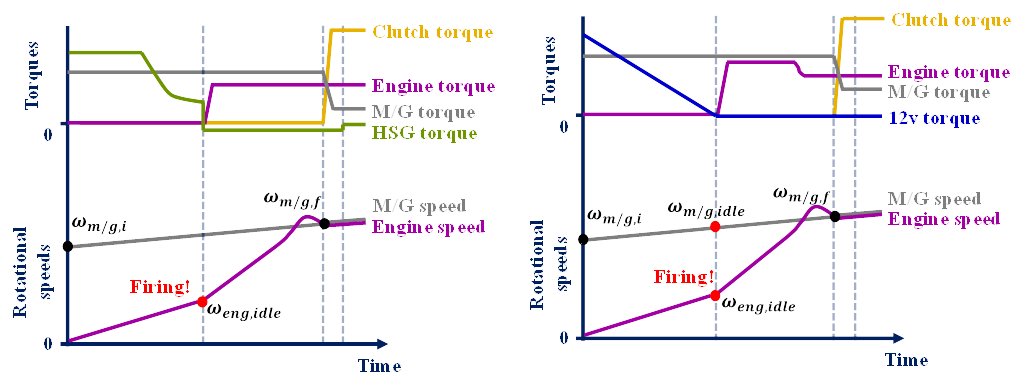
Overview of the P0-P2 engine-start control strategy (좌), Overview of the 12v+P2 engine-start control strategy(우)
- Such architectural variations pose a design trade-off between cost and engine-start performance. Therefore, we systematically evaluated the optimal engine-start performance of some parallel HEVs with various starters and compared the considered architectures considering both the cost and engine-start performance.



